Security-enhancing technologies for the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is growing exponentially, with 25 billion devices expected to be deployed by 2030. However, the more devices that are installed and connected to the Internet without adequate security measures, the greater the number of cyberattacks will be. Therefore, new cryptographic algorithms and protocols need to be designed and developed for IoT devices and ecosystems that typically use cloud technology. In our research, we address, among others, secure pseudorandom number generation in resource-constrained environments. We have also developed the WebAssembly-based CryptID package, which provides identity-based encryption and digital signature solutions for microcontrollers. We are also exploring mutual entity authentication protocols for IoT ecosystems and cloud environments, taking into account the distributed nature of the service. We apply provable security methods to verify whether a cryptographic protocol meets its security requirements. We also use technologies based on computational and formal methods.
Related projects:
- Security classification of Internet of Things devices, National Laboratory of Infocommunication and Informatics (InfoLab) (National Security Service, Alverad Technology Focus), 2022–2023
- Security Enhancing Technologies for the Internet of Things (SETIT), Project no. 2018-1.2.1-NKP-2018-00004, 2018–2022
- Securing Cloud Authentication, HU-MATHS-IN (Hungarian Mathematical Service Network in Industry and Innovation) EFOP-3.6.2-16-2017-00015, 2017–2021
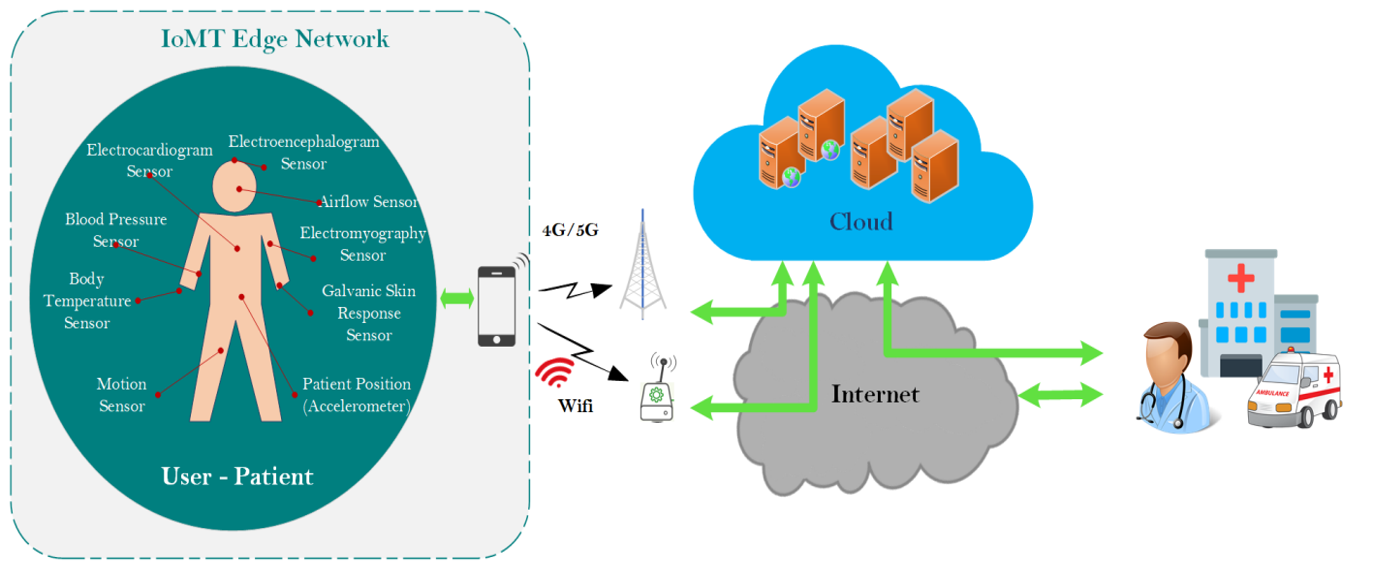
Anonymity and its applications
Various regulations (such as the GDPR) require the protection of user privacy, which is increasing the need to design privacy-preserving cryptographic protocols and algorithms. There are many applications where users do not want to reveal their identity. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in research on vehicular ad-hoc networks (VANETs). In the VANET environment, we focus on secure, anonymous messaging solutions. Sender anonymity is essential for e-voting—where it is necessary to ensure that only those entitled to vote have the right to vote while remaining unidentifiable—and for e-examination systems, where the examinee and the examiner are mutually unknown to each other. A number of algorithms and protocols have been developed to solve these problems. We use provable security methods to verify that a cryptographic protocol satisfies its security requirements. We also use technologies based on computational and formal methods.
Related projects:
- Secure Communication for VANETs Automotive project, TKP2020-NKA-04, National Research, Development and Innovation Fund, 2020–2022
- Development of a credible and anonymous exam correction system, GOP-1.1.2-07/1-2008-0001 (NetLock CA), 2008–2011



Identity-based cryptography
In 1984, Adi Shamir introduced the concept of identity-based cryptography. The idea is to use user identities, such as email addresses or phone numbers, as public keys instead of generating and managing digital certificates. We have developed the WebAssembly-based CryptID suite, which provides identity-based encryption and digital signature solutions for microcontrollers, mobile devices, and desktops. We are designing cryptographic protocols using identity-based keys to significantly reduce the time complexity of protocol operations. We have designed a remote password registration and entity authentication system that achieves improved efficiency. We use provable security methods to verify whether a cryptographic protocol meets its security requirements. We also use technologies based on computational and formal methods.
Blockchain
Our research group examines the technological implementation of blockchain and its possible areas of application, paying particular attention to security aspects, such as the availability of decentralized systems. Our goal is to develop innovative solutions, which also include transaction handling, smart contracts, and digital identity management. In the course of our research, we analyze the vulnerabilities, consensus mechanisms, and cryptographic primitives of distributed ledger technologies, as well as develop new methods to increase the efficiency and resilience of blockchain-based systems.
Related projects:
- 1,080,000,000 HUF was awarded to the consortium implementing the DigitalTech EDIH project within the framework of Government Decision 1612/2022 (XII. 13.) on increasing Hungarian participation in directly managed EU programmes and ensuring the own-resource costs of certain direct EU tenders.